Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and osteoarthritis (OA) are two of the most common forms of arthritis, a group of chronic conditions that affect the joints and cause pain, stiffness, and inflammation. While both conditions share some similarities, they differ in several key ways. In this article, we will explore the differences and similarities between RA and OA.
What is Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)?
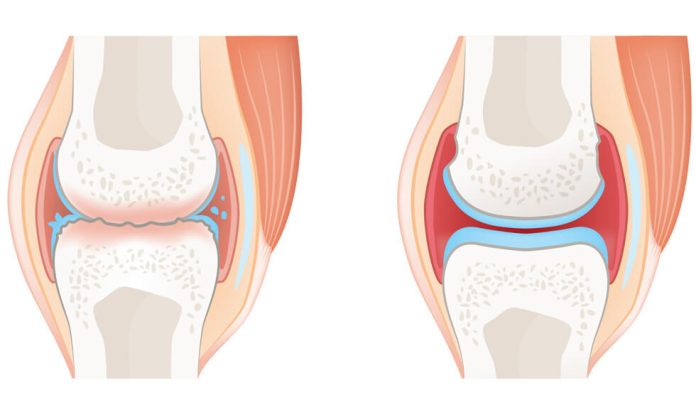
Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disorder in which the body’s immune system attacks the lining of the joints, causing inflammation and damage. It typically affects the small joints in the hands and feet but can also affect other joints throughout the body, including the hips, knees, shoulders, and elbows. RA can cause joint deformity, loss of mobility, and significant pain.
What is Osteoarthritis (OA)?
Osteoarthritis, on the other hand, is a degenerative joint disease that occurs when the cartilage that cushions the joints wears away over time. It is most common in weight-bearing joints, such as the hips, knees, and spine, and tends to occur later in life. OA can cause joint pain, stiffness, and swelling, as well as bone spurs and joint deformity.
Key Differences between RA and OA
- Causes
RA is an autoimmune disorder, which means that it is caused by the body’s immune system attacking its own tissues. OA, on the other hand, is caused by wear and tear on the joints over time.
- Onset
RA typically develops in middle age, while OA tends to occur later in life.
- Joint Involvement
RA tends to affect the small joints in the hands and feet, while OA is more common in weight-bearing joints such as the hips and knees.
- Symptom Progression
RA can progress quickly and aggressively, causing joint damage and deformity within months. OA tends to progress more slowly over time, with symptoms worsening gradually over several years.
- Systemic Symptoms
RA can cause systemic symptoms such as fatigue, fever, and weight loss. OA typically does not cause these symptoms.
Key Similarities between RA and OA
- Joint Pain and Stiffness
Both RA and OA cause joint pain, stiffness, and swelling, which can make it difficult to move around and perform daily activities.
- Chronic Conditions
Both RA and OA are chronic conditions, which means that they are long-lasting and typically require ongoing management.
- Treatment Options
Treatment options for both RA and OA include pain management, physical therapy, and medications such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs).
In conclusion, while RA and OA share some similarities, they are two distinct conditions that differ in terms of their causes, onset, joint involvement, symptom progression, and systemic symptoms. It is important to accurately diagnose and differentiate between these two conditions in order to provide appropriate treatment and management. If you are experiencing joint pain, stiffness, or other symptoms, it is important to speak with your healthcare provider to determine the underlying cause and develop an appropriate treatment plan.