Probiotics are organisms such as bacteria or yeast that naturally occurs in the gut. Probiotics are available in supplements and foods.
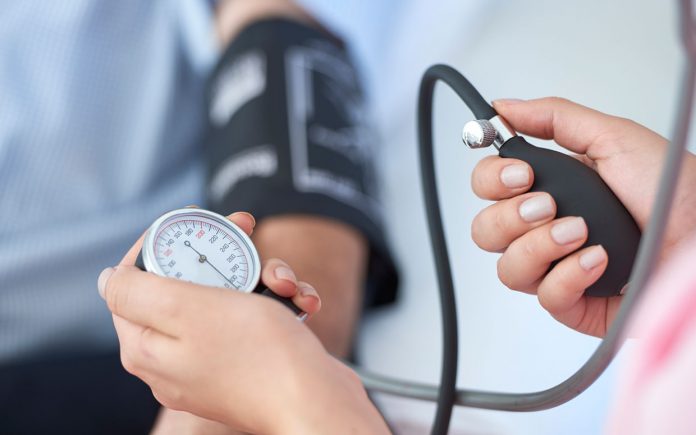
Past human clinical trials have shown that probiotic consumption may improve blood pressure control. In a systematic review Dr. Jing Sun, PhD, lead author and senior lecturer at the Griffith Health Institute and School of Medicine, Griffith University, Gold Coast, Queensland, Australia and colleagues set out to clarify the effects of probiotics on blood pressure using a meta-analysis of randomized, controlled trials.\
The research team searched data bases which included and Clinicaltrial.gov and PubMed to identify eligible articles. Nine trials randomized controlled trials were included. The trails had examined the effects of probiotic products with live cultures in 543 adults with and without hypertension.
The trails were widely diverse with three of the trials that included only healthy participants who were free of hypertension, two trails had patients with high cholesterol, one done sole y with hypertension, one with overweight or obese participants and one with metabolic syndrome.
The interventions in these studies were considerably different, four studies had used yogurt for the probiotic source, two studies used fermented and sour milk, one used probiotic supplement capsules, ne used probiotic rose-hip drinks and one used probiotic cheese.
Four studies used a single species of probiotic bacteria; the rest used combinations of two or three strains. The total daily dose ranged from 109 to 1012 colony-forming units (CFU). The studies durations were three to nine weeks .
The researchers found probiotic consumption lowered systolic blood pressure (the top number) by an average 3.56 millimeters of mercury (mm Hg) and diastolic blood pressure (the lower number) by an average 2.38 mm Hg, compared to the control group (did not consume probiotics).
The effect of probiotics on diastolic pressure was greatest in participants who had a blood pressure equal to or greater than 130/85.
Consuming probiotics for less than eight weeks did not lower systolic or diastolic blood pressure.
Participants who had normal blood pressure at baseline had shown no substantial improvement in blood pressure.
According to the researchers this meta-analysis suggests that consuming probiotics may improve BP by a modest degree, with a potentially greater effect when baseline BP is elevated, multiple species of probiotics are consumed, the duration of intervention is eight weeks or more or daily consumption dose is 10 or more CFU.
Dr. Sun commented “We believe probiotics might help lower blood pressure by having other positive effects on health, including improving total cholesterol and low-density lipoprotein, or LDL, cholesterol; reducing blood glucose and insulin resistance; and by helping to regulate the hormone system that regulates blood pressure and fluid balance.”
Dr. Sun continued “The studies looking at probiotics and blood pressure tend to be small.” “Moreover, two studies had a short duration of three to four weeks of probiotic consumption, which might have affected the overall results of the analysis.”
Additional studies are needed before doctors can confidently recommend probiotics for high blood pressure control and prevention, she said.
This study appears in the American Heart Association journal Hypertension.