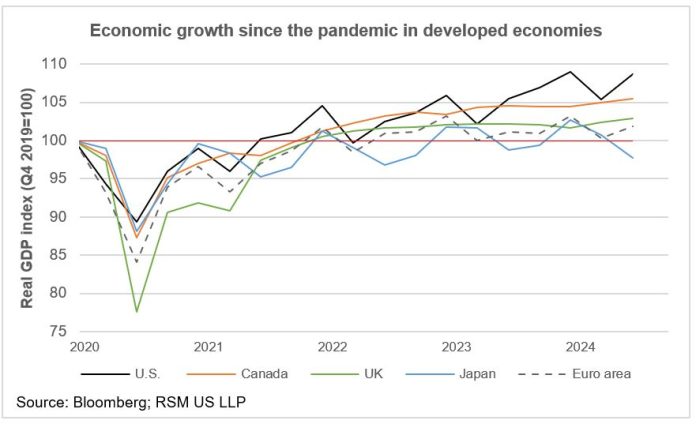
With the U.S. economy growing over 3%, what’s driving this impressive surge? How does this compare to previous periods, and what could it mean for inflation and interest rates? I’m curious about how this growth might affect my personal finances, job opportunities, or investment decisions, and if there are any potential risks I should be aware of.
The U.S. economy has recently seen an impressive growth rate of over 3%, sparking interest among economists, investors, and everyday Americans. This surge, which marks a significant rebound, raises questions about what’s driving the growth, how it compares to previous periods, and what it could mean for inflation, interest rates, and personal financial decisions. If you’re wondering how this growth could impact your job, investments, or household budget, keep reading for an in-depth look at the current economic landscape.
Table of Contents
Toggle1. What’s Behind the 3% Economic Growth Surge?
Strong Consumer Spending
One of the primary factors driving the U.S. economy’s impressive growth is robust consumer spending. As the nation emerges from the pandemic and restrictions continue to ease, Americans are spending more on goods and services. Key sectors contributing to this surge include retail, real estate, and leisure activities, where consumers are eager to make up for lost time and expenditures during lockdown periods.
Business Investment and Innovation
Alongside consumer spending, business investment has played a significant role in this growth. Companies have been increasing spending on technology, infrastructure, and expansion. Innovations in the tech sector and large-scale projects in construction and manufacturing are helping to boost productivity, leading to a more vibrant economic environment.
Government Stimulus and Fiscal Policies
Government spending, including various stimulus packages and fiscal policies, also continues to support the economy. Investments in infrastructure projects, healthcare, and clean energy have provided a boost, particularly in areas where long-term gains are expected.
The Labor Market Recovery
The labor market has seen strong improvements, with unemployment rates dropping and wages rising in many sectors. A tight labor market has pushed businesses to offer better pay and incentives to attract talent, which in turn supports consumer spending and economic growth.
2. How Does This Growth Compare to Previous Periods?
The Post-Pandemic Rebound
This economic surge comes after a challenging period marked by the global pandemic. In comparison to previous years, the growth rate of over 3% is impressive, as it outpaces growth seen during the pre-pandemic era. However, much of this growth can be attributed to the recovery from the economic downturn caused by the pandemic. In 2020, the economy contracted significantly, so this rebound is, in part, a return to normal.
Looking at the last few decades, the growth rate is relatively strong but still below the levels seen in the 1990s and early 2000s, when the economy routinely posted annual growth rates of 4% or higher.
Historic Comparisons
While the current 3% growth is commendable, it’s important to keep historical trends in mind. The 2008 financial crisis saw a prolonged period of slow growth, while the dot-com bubble and housing market crashes also created volatility. These events led to deep recessions, making this current growth period a significant recovery, but not an unprecedented boom.
3. What Does This Growth Mean for Inflation and Interest Rates?
The Risk of Inflation
The surge in economic activity has raised concerns about inflation. Increased consumer demand and rising wages can lead to higher prices for goods and services, particularly in sectors that have been impacted by supply chain bottlenecks and labor shortages. As inflation rises, the purchasing power of your money decreases, meaning you may pay more for everyday items like food, gas, and rent.
Interest Rate Hikes
To counteract inflation, the Federal Reserve may choose to raise interest rates. Higher rates typically lead to more expensive borrowing costs for individuals and businesses, as it increases the cost of loans and mortgages. While this is an attempt to keep inflation in check, higher interest rates can slow down economic growth by discouraging spending and borrowing.
Balancing Growth and Stability
The challenge for policymakers will be to balance economic growth with the risk of runaway inflation. If inflation continues to rise, we might see a tightening of fiscal policies, but if growth starts to slow, the Federal Reserve could adjust rates to ensure that the economy doesn’t lose momentum.
4. What This Means for Your Personal Finances
Impact on Savings and Investments
If you’re an investor, the strong economic growth could lead to higher stock market returns, particularly in sectors like technology, consumer goods, and real estate. However, if inflation increases significantly, this could erode the value of fixed income investments like bonds. It’s essential to stay diversified and be prepared for potential volatility as interest rates rise.
Job Opportunities and Wage Growth
On the employment front, the surge in economic activity has led to increased demand for workers, particularly in industries like technology, healthcare, and construction. If you’re seeking a job, this could present opportunities for higher wages and better benefits. However, the competition for skilled workers will likely increase, especially as businesses seek to capitalize on the recovery.
Real Estate and Housing Market
The housing market has been booming, but rising interest rates could make mortgages more expensive, potentially cooling off demand in the real estate sector. If you’re planning to buy a home, higher rates could affect your monthly payments, so it’s wise to lock in a rate soon before further hikes.
5. Potential Risks to Be Aware Of
Rising Debt Levels
As economic growth continues, there’s the risk that consumer debt and business borrowing could escalate. If people and companies take on too much debt during this period of growth, it could lead to financial instability if conditions shift, such as a recession or higher interest rates.
Global Economic Uncertainty
The global landscape remains uncertain. Trade tensions, geopolitical risks, and other global crises can affect U.S. markets and economy, potentially slowing down the impressive growth we’re witnessing. Keeping an eye on international developments is crucial for understanding potential risks to economic stability.
6.What Should You Do with This Knowledge?
The U.S. economy’s impressive growth rate of over 3% is a sign of strong recovery, but it also comes with risks like inflation and the potential for rising interest rates. As an individual, this surge may mean better job opportunities, higher wages, and stronger investment returns—but it’s crucial to stay vigilant and manage your finances wisely. Be aware of potential inflation and the impact of higher borrowing costs, and consider adjusting your savings, investments, and housing plans to mitigate these risks. Understanding these dynamics will help you make more informed decisions in the ever-changing economic environment.